

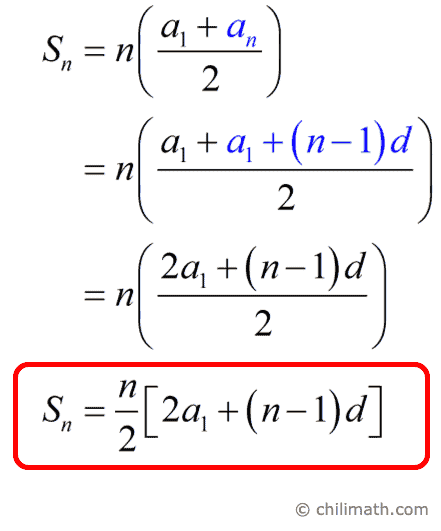
Certain progressions follow a general rule or formula for evaluating the sum of numbers or the unknown term, thereby greatly reducing the stress and need for difficult and tedious calculations.
FORMULAS FOR ARITHMETIC SEQUENCES SERIES
The formulas for the different series help in predictive analysis in other fields sloping to make better decisions by monitoring the outcome. It helps in calculating unknown values when the pattern or the set of rules that a system follows is known. Understanding Arithmetic sequences and series formulas are integral to understanding patterns in number sequences. Calculate the sum of the first 20 terms and calculate the 10th term for the given A.P. Here are the formulas related to the arithmetic sequence. Consider an arithmetic sequence where the first term is a₁ (or ‘a’), and the common difference is d. To find the sum of its first n terms, we calculate the sum of the Arithmetic Sequence Formula. This directly follows from the understanding that the arithmetic sequence a₁, a₂, a₃, … = a₁, a₁ + d, a₁ + 2d, a₁ + 3d,… In an arithmetic sequence, it is also known as a general term. The nth term of an arithmetic sequence a₁, a₂, a₃, … is given by aₙ = a₁ + (n – 1) d. Here, the “fixed number” is called the “common difference” and is denoted by ‘d’, and the formula for the common difference is d = aₙ – aₙ₋₁. We have already seen that in an arithmetic sequence, each term, except the first term, is obtained by adding a fixed number to its previous term. For example, in the sequences 4, 8, 12, 16, … the first term is 4, i.e., a₁ = 4 (or) a = 4 Common Difference of Arithmetic Sequence The first number in an Arithmetic Sequence is known as its First Term. Given below are the universally accepted terminology in Arithmetic Sequence used by one and all, a 1, a 2, a 3, a 4……. Given below are a few more examples of Arithmetic Sequences:
FORMULAS FOR ARITHMETIC SEQUENCES VERIFICATION
Thus, an arithmetic sequence can be written as a, a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d,… The verification for the above-given series formula can be written as:-Ī, a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d, a + 4d, … = 6, 6 + 6, 6 + 2(6), 6 + 3(6), 6 + 4(6),… = 6, 12, 18, 24, 30,…. is an arithmetic sequence because every term is obtained by adding a constant number (6) to its previous term. Let’s take an example for a better understanding To find the sum of the first n terms of Arithmetic Sequencesĭ = common difference between terms Arithmetic Sequences Example To find the n th term of an Arithmetic Sequences There are two Arithmetic Sequence formulas:. Hence the series is said to be an Arithmetic Sequence. In the given series, there is a pattern that can be seen which is that the difference between every two consecutive numbers is 4. Let us now discuss the series and sequence formula. These sequences and series can be classified into arithmetic progression. The order of elements or terms is important in a sequence but not in a series. Therefore, a series is the sum of terms in a progression. These individual terms of a sequence, when added together, give rise to a series. A sequence, also called a progression, is defined as the arrangement of individual terms in an orderly manner. Understanding Arithmetic sequences and series is a crucial part of studying mathematics as it is applicable in various fields such as computer programming, finance, statistics and physics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
